polarimeter chemistry definition|what to use polarimeter for : distributor Polarimeter is the instrument used to determine the specific rotation of a compound. It consists of the following: monochromatic light source; polarizer, a prism that . Resultado da 12 de fev. de 2024 · Access movies and series on demand, plus 24/7 live channels. Continue watching to jump back in to shows and movies you’ve already started, download and .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBNew Canadian customers outside of Ontario only. Opt-in required within registration .
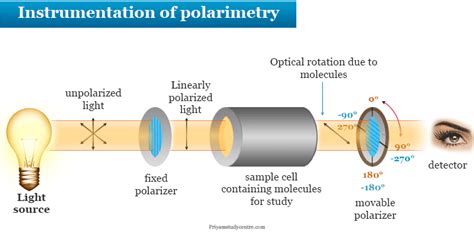
A polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure optical rotation: the angle of rotation caused by passing linearly polarized light through an optically active substance. Some chemical substances are optically active, and linearly polarized (uni-directional) light will rotate either to the left (counter-clockwise) or right (clockw. Polarimeter is the instrument used to determine the specific rotation of a compound. It consists of the following: monochromatic light source; polarizer, a prism that .
In measuring optical rotation, plane-polarized light travels down a long tube containing the sample. If it is a liquid, the sample may be placed in the tube as a pure liquid .A polarimeter is an instrument which measures the angle of rotation by passing polarized light through an optically active (chiral) substance. To measure optical rotation, a Light Emitting Diode (LED) produces a beam of . Polarimetry. updated. Most physical properties of enantiomers i.e., melting point, boiling point, refractive index, etc. are identical. However, they differ in a property called optical .Definition. A polarimeter is an instrument used to measure the optical activity of a substance, which is the ability of a material to rotate the plane of polarized light. It is a crucial tool in the .
Polarimetry, in analytic chemistry, measurement of the angle of rotation of the plane of polarized light (that is, a beam of light in which the vibrations of the electromagnetic waves .
A sample containing a single enantiomer of fluoxetine (Prozac) is placed in a polarimeter. The observed rotation is 9.06 ° clockwise. The sample was made by dissolving 1.24 g of fluoxetine in a solution with a total volume of .Polarimetry machines are used in chemistry in a variety of ways. Their primary use is to measure the angle of rotation of an optically active substance using polarized light.
polarimetry, in analytic chemistry, measurement of the angle of rotation of the plane of polarized light (that is, a beam of light in which the vibrations of the electromagnetic waves are confined to one plane) that results upon its passage through certain transparent materials. Polarimetry is of interest to the chemist because the ability of a .
Measurement of Optical Rotation . Polarimeter is the instrument that measures the direction and angles of rotation of plane-polarized light. The plane-polarized light pass through the sample tube containing the solution of .
Here is a diagram of a modern polarimeter. Image source: wikipedia . The Journal of Organic Chemistry 1970, 35 (9), 2849-2867 DOI: 1021/jo00834a001 These can be considered as the official IUPAC rules for .Polarimeter analyzers for a wide range of applications. Polarimetry is one of the most important quality control methods in the pharmaceutical, chemical, cosmetics, food and beverage industries. The angle of rotation allows you to ascertain the identity and quality of substances as well as their concentration in mixtures. It is also pssible to .
Planetary Satellites, Natural. Bonnie J. Buratti, in Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (Third Edition), 2003 III.A.4 Polarimetry. Polarimetry is the measurement of the degree of polarization of radiation reflected from a satellite's surface. The polarization characteristics depend on the shape, size, and optical properties of the surface particles. In measuring optical rotation, plane-polarized light travels down a long tube containing the sample. If it is a liquid, the sample may be placed in the tube as a pure liquid (its is sometimes called .
An easily constructed and inexpensive polarimeter with an optical rotation angle resolution of about 0.5° is presented. It is made from small pieces of polarizing film, 2 LEDs, a protractor, and a few wires, all held in place with plastic interlocking toy bricks, such as Lego bricks. The instrument was used to demonstrate the optical rotation of plane polarized light as .Principle of the polarimeter: The basic operating principle of a polarimeter includes a source that produces light with a specifically prepared linear polarization state, usually by passing through a polarizer. The light is transmitted by an optically active sample which often rotates the direction of polarization. . Chemistry; Principle and .
In a polarimeter (figure 2), plane-polarized light is introduced to a tube (typically 10 cm in length, figure 3) containing a solution with the substance to be measured. If the substance is optical inactive, the plane of the polarized light will not change in orientation and the observer will read an angle of [α]= 0 o. If the compound in the . Automatic Polarimeter: This type of polarimeter uses a digital display to measure the degree of polarization. It is commonly used in pharmaceuticals and chemistry. Polarimeter Spectrometer: This type of polarimeter is used to measure the optical activity of a sample over a wide range of wavelengths. It is commonly used in physics and chemistry.Polarimeter Light Sources. It is now common practice to use other light sources such as xenon or tungsten halogen. With appropriate filters, these light sources offer advantages of cost, long life, and broad wavelength emission range over traditional light sources. Polarimeters measure the observed rotation designated by the Greek lower case .
Polarimeter: A device used to measure the amount and direction that a substance rotates plane polarized light.A polarimeter consists of a light source, a monochromator (filters out all but a specific wavelength of light), a polarizer (converts the light beam to plane polarized light), a sample tube (holds the sample being measured), a second polarizer (to determine the degree .
General Chemistry Structure & Reactivity in Organic, Biological and Inorganic Chemistry (Schaller) Structure & Reactivity in Organic, Biological and Inorganic Chemistry I: Chemical Structure and Properties 5: Stereochemistry 5.8: The Polarimetry Experiment .The polarimeter is an instrument that measures the direction and angles of rotation of plane-polarized light. The plane-polarized light passes through the sample tube containing the solution of a sample, and the angle of rotations will be received and recorded by the analyzer, as summarized in Fig. 5.4c.. Figure 5.4c Measurement of Optical Rotation with Polarimeter
A. standardized specific rotation value, polarimeter B. observed rotation, standardized specific rotation value . Mutarotation in Chemistry: Definition, Mechanism & ExamplesOptical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circular birefringence and circular dichroism are the manifestations of optical activity.Optical activity occurs only in chiral materials, those lacking .
A polarimeter is a device that measures the rotation of linearly polarized light by an optically active sample. This is of interest to organic chemists because it enables differentiation between optically active stereoisomers, i.e., .Recording optical rotation with a polarimeter: The plane of polarisation of plane polarised light (4) rotates (6) as it passes through an optically active sample (5).This angle is determined with a rotatable polarizing filter (7).. In chemistry, specific rotation ([α]) is a property of a chiral chemical compound. [1]: 244 It is defined as the change in orientation of monochromatic plane . Various devices play an important role in measuring and quantifying various features of substances in the field of scientific analysis. A polarimeter is one such piece of equipment that is useful in the fields of optics and chemistry.It allows scientists and researchers to explore how light interacts with optically active compounds.
Observed rotation of an optically active compound, measured using the polarimeter, depends on the experimental conditions and, therefore, is not a characteristic property of the compound. Specific rotation (symbol: [α] λ T) of an optically active compound is defined as follows: α = observed rotation measured using a polarimeter Optical isomerism. Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same structural formula but have the atoms arranged differently in space There are two types of stereoisomerism. Geometrical (E/Z) Optical; A carbon atom that has four different atoms or groups of atoms attached to it is called a chiral carbon or chiral centre. Chira comes from a Greek word .Diastereomers - Stereoisomeric compounds that are not enantiomers are called diastereomers. Diastereomers which are achiral, the majority of diastereomeric compounds are chiral compounds which have more than one chiral center. Visit BYJUS to learn more about Diastereomers.
Polarimetry, using a flow-through polarimeter at 589 nm, is the general method of sucrose analysis in bulk raw and white sugars. Traditional polarimeters are being replacing by polarimeters using light of longer wavelengths, λ =880 nm, which can be used for monitoring a colored (through not a turbid) solution, and so decreases solid waste .Polarimeter definition: An instrument used to measure the rotation of the plane of polarization of polarized light passing through an optical structure or sample.Polarimetry machines are used in chemistry in a variety of ways. Their primary use is to measure the angle of rotation of an optically active substance using polarized light. . The step by step process of rotation of plane-polarized light in a polarimeter is depicted by the schematic diagram below: The specific rotation value of a chiral .Anisotropic crystalline solids, and samples containing an excess of one enantiomer of a chiral molecule, can rotate the orientation of plane-polarized light. Such substances are said to have optical activity.Measurement of this change in polarization orientation is called polarimetry, and the measuring instrument is called a polarimeter.These measurements are useful for studying .
Optical Activity. Optical activity of an organic compound refers to the property of an organic compound by the virtue of which, it rotates the plane polarised light (produced by passing ordinary light through Nicol prism) when it is passed through their solutions and the compounds are known as optically active compounds.. The optical activity of the substance is a measure of the .
why polarimeter is used
which lamp used in polarimeter
Resultado das Loterias Estaduais (Jogo do Bicho) PT Rio. D.
polarimeter chemistry definition|what to use polarimeter for